Toggle light
Comments
94 Views
Report
Favorite
If current server doesn't work please try other servers below.

Score: 10 / 5 rated
Corporate Finance Understanding the Basics, Importance, and Key Concepts
Corporate Finance: Understanding the Basics, Importance, and Key Concepts
In today’s dynamic and fast-paced business world, effective financial management is essential for companies to thrive and grow. Corporate finance plays a crucial role in the strategic decision-making process of businesses, as it focuses on how companies acquire, manage, and allocate their resources to maximize profitability and shareholder value. Whether a small startup or a multinational corporation, corporate finance is at the heart of every successful organization’s financial health.
In this article, we will explore the fundamental principles of corporate finance, key concepts and tools used, the importance of corporate finance in business operations, and the roles it plays in determining a company’s success. If you are an aspiring entrepreneur, a business student, or simply someone interested in how companies handle their financial matters, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into corporate finance.
What Is Corporate Finance?
Corporate finance refers to the financial activities and decisions that companies make in order to fund their operations, maximize profits, and increase shareholder value. It includes everything from managing day-to-day cash flow to deciding on long-term investments and capital structures. The ultimate goal of corporate finance is to make the best possible financial decisions to ensure a company’s growth, stability, and sustainability.
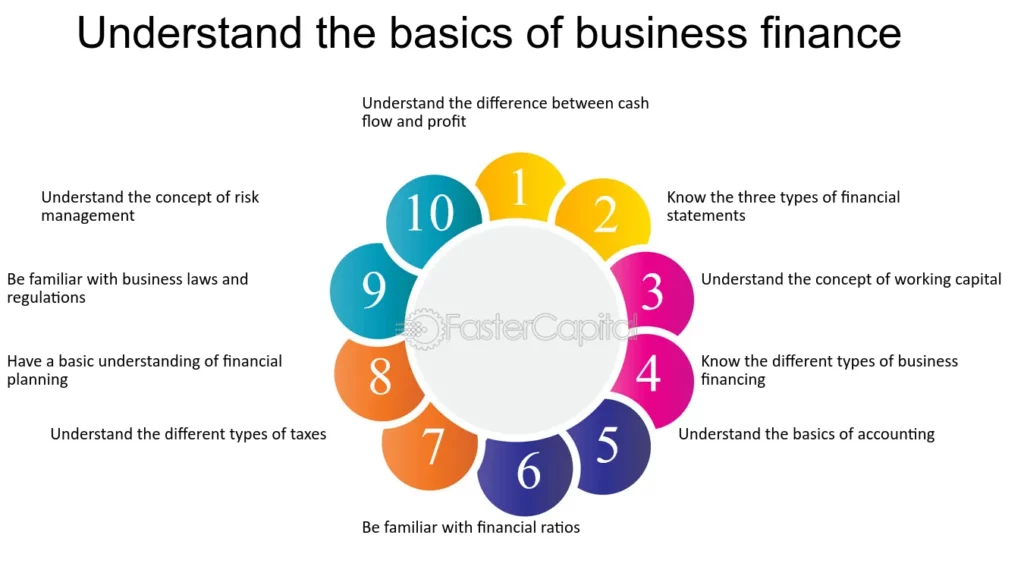
Corporate finance is typically divided into three major areas:
- Capital Budgeting: The process of planning and evaluating investments and major capital expenditures.
- Capital Structure: The decision-making process regarding the mixture of debt and equity financing a company uses.
- Working Capital Management: The management of a company’s short-term assets and liabilities to ensure sufficient liquidity for operations.
The Role of Corporate Finance in Business
Corporate finance has a wide-reaching impact on almost every aspect of a business. Here’s how corporate finance functions in different areas:
- Investment Decisions (Capital Budgeting): Every company needs to make decisions about how to invest its resources. Capital budgeting helps determine which projects or investments are worth pursuing. It involves evaluating potential returns on investment (ROI) and assessing the risk and cost associated with different ventures.For example, a company may consider investing in new technology, expanding its operations, or launching a new product line. Corporate finance helps assess the financial feasibility of these decisions through techniques such as Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), and Payback Period.
- Financing Decisions (Capital Structure): Companies need to determine how to raise capital to fund their operations. Corporate finance helps them decide between using debt (loans or bonds) or equity (issuing shares of stock). The ideal capital structure will vary depending on the company’s size, industry, risk tolerance, and market conditions.The goal is to strike a balance between debt and equity to minimize the cost of capital while maintaining control over the business. Too much debt can be risky, while too much equity dilution may reduce the value of existing shareholders.
- Cash Flow and Liquidity Management (Working Capital Management): Proper cash flow management is crucial to keep a business running smoothly. Corporate finance involves the management of working capital, which includes short-term assets like inventory and receivables, and short-term liabilities like accounts payable.A company must maintain enough liquidity to meet its short-term obligations and avoid cash shortages that could disrupt operations. Corporate finance ensures that the company optimizes its cash flow by carefully managing its receivables, payables, inventory, and other current assets.
- Profit Maximization and Shareholder Value: One of the most important goals of corporate finance is to maximize the company’s profitability and, in turn, enhance shareholder value. This involves making strategic decisions that increase profits while managing costs, risks, and resource allocation efficiently.Corporate finance works closely with the company’s strategy to ensure long-term value creation. This could include mergers and acquisitions, financial restructuring, or other strategies that drive growth and profitability.
Key Concepts in Corporate Finance
Corporate finance uses a wide range of concepts and tools to make informed decisions. Below are some key principles and concepts that are essential for understanding corporate finance.
1. Time Value of Money (TVM)
The Time Value of Money is a fundamental principle in corporate finance, which states that a dollar today is worth more than a dollar in the future. This is because money has the potential to earn interest or generate returns over time.
To make investment decisions, corporate finance professionals use TVM concepts like Present Value (PV), Future Value (FV), and Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) to calculate the worth of future cash flows today.
2. Cost of Capital
The cost of capital refers to the rate of return that a company must offer to persuade investors to fund the company’s projects or operations. It is used to assess the feasibility of investments and capital projects.
The cost of capital is typically calculated using the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC), which combines the cost of debt and the cost of equity in a proportion that reflects the company’s capital structure.
3. Risk and Return
Risk and return are two key factors that every corporate finance professional must consider when making financial decisions. Higher risk often leads to higher potential returns, but it also increases the likelihood of losses.
In corporate finance, risk is measured in several ways, such as through volatility, beta coefficients (in the case of stock market investments), and other risk metrics. The goal is to find investments or financial decisions that balance risk and reward in line with the company’s objectives.
4. Leverage
Leverage refers to the use of debt to finance business operations or investments. It allows companies to amplify their returns, but it also comes with the risk of magnifying losses. Leverage is often used to enhance profitability when the return on investments exceeds the cost of debt.
Corporate finance professionals need to carefully assess a company’s level of leverage to ensure it doesn’t become overburdened by debt.
5. Capital Budgeting Techniques
Capital budgeting is the process of evaluating long-term investments to determine their profitability and feasibility. The most common methods used in corporate finance for capital budgeting include:
- Net Present Value (NPV): NPV measures the profitability of an investment by calculating the difference between the present value of expected cash flows and the initial investment cost. A positive NPV indicates a good investment opportunity.
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR): IRR is the rate at which an investment’s NPV equals zero. It helps identify the percentage return that can be expected from an investment.
- Payback Period: This method calculates the time it will take for an investment to repay its initial cost. A shorter payback period is generally more favorable.
The Importance of Corporate Finance
Corporate finance is essential for a company’s growth and success, as it directly impacts various aspects of business operations. Here are some key reasons why corporate finance is important:
- Optimal Capital Allocation: One of the primary functions of corporate finance is to ensure that a company’s capital is allocated efficiently. With the right allocation, businesses can maximize returns on investments, minimize wastage, and fund profitable projects that align with their long-term strategy.
- Risk Management: Every business faces some level of risk, whether it’s market fluctuations, changes in customer behavior, or operational risks. Corporate finance professionals help manage these risks by implementing hedging strategies, using derivatives, and diversifying investments to protect the company from financial instability.
- Sustaining Growth: Corporate finance helps companies sustain growth by analyzing new investment opportunities, securing funding, and optimizing operational efficiency. Financial decisions, such as mergers and acquisitions, can also contribute to the company’s expansion and market presence.
- Maximizing Shareholder Value: The ultimate goal of corporate finance is to increase shareholder wealth by improving profitability, achieving sustainable growth, and making strategic financial decisions. Whether through dividends or capital appreciation, corporate finance aims to provide maximum value to shareholders.
- Financial Health and Stability: Managing a company’s finances wisely ensures long-term financial stability. Effective cash flow management, appropriate financing, and balanced capital structures all contribute to a company’s ability to withstand economic downturns and capitalize on favorable market conditions.
Corporate Finance in Action: Case Studies
To better understand corporate finance in practice, let’s look at two example scenarios where corporate finance plays a pivotal role in decision-making.
Case Study 1: Investment Decision in Technology
A company is considering investing in a new technology to streamline operations and improve productivity. Corporate finance professionals would conduct an NPV analysis to assess the expected cash inflows and costs associated with the investment. They would also evaluate the IRR to ensure it exceeds the company’s cost of capital, ensuring that the investment will generate value for shareholders.
Case Study 2: Financing Decision for Expansion
A business is looking to expand its operations by opening new stores in different regions. The company must decide whether to raise funds through debt (such as issuing bonds) or equity (issuing more shares). Corporate finance professionals would analyze the cost of debt versus the potential dilution of ownership through equity. The company might decide to use a combination of both to maintain financial flexibility and minimize the risks associated with heavy borrowing.
Conclusion
Corporate finance is at the core of every successful business. It encompasses the decision-making processes that determine how companies raise, manage, and invest their financial resources to maximize profitability and growth. Whether it’s deciding on a new investment, structuring capital efficiently, or managing cash flow, corporate finance is essential to achieving business goals and enhancing shareholder value.
For business leaders, entrepreneurs, and students interested in corporate finance, understanding these concepts is crucial to making informed financial decisions that drive success. By mastering the tools and principles of corporate finance, you can contribute to the long-term stability and growth of any organization.
Post Views: 6
Genre: Blog
Director:
You may also like
Report Content
Corporate Finance Understanding the Basics, Importance, and Key Concepts
Movie